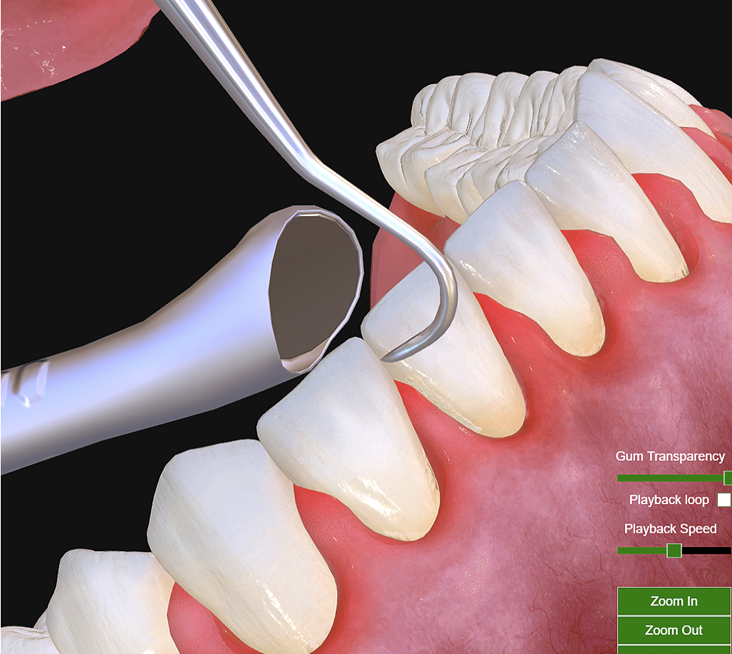
The Joint Commission on National Dental Examinations (JCNDE) has launched the Dental Hygiene Licensure Objective Structured Clinical Examination (DHLOSCE). The purpose of the examination is to provide licensing jurisdictions with a valid, reliable, and fair means of determining whether candidates have the level of clinical judgment and skills required to safely practice dental hygiene.
The DHLOSCE is a professionally developed examination that assesses whether candidates can apply their clinical judgment and skills in a problem-solving context, at the level of proficiency required for safe practice.
Dental Hygiene Licensure Objective Structured Clinical Examination (DHLOSCE™)
About the DHLOSCE
Practice questions were developed by test constructors involved in creating the examination and represent the types of questions that will be on the DHLOSCE. The preview also has instructions on using 3D images.
See the individual state board licensing jurisdictions below.
More about the DHLOSCE
Additional Resources
DHLOSCE Webinar and Preview Presentation
A webinar on the Dental Hygiene Licensure Objective Structured Clinical Examination (DHLOSCE) was held for dental students on December 8, 2025. The webinar was hosted by Ms. Tami J. Grzesikowski and Dr. Waldschmidt, who presented information regarding the DHLOSCE examination, the Incentive Plan, and a DHLOSCE Preview.
Watch the webinar
Differences between the NBDHE and DHLOSCE
Compare the differences between the National Board Dental Hygiene Examination (NBDHE) and the Dental Hygiene Licensure Objective Structured Examination (DHLOSCE).
State dental board members and dental hygiene program directors download this file: NBDHE vs. DHLOSCE (PDF)
Exam Candidates download this file: NBDHE VS. DHLOSCE (PDF)
ADEA Poster Presentation
Review this poster for key examination information about both the DLOSCE and DHLOSCE to be presented at the ADEA March conference.
View the Poster Presentation (PDF)
Updates on JCNDE Examination Programs: The NBDHE and DHLOSCE
A webinar on the JCNDE Dental Hygiene Examination Programs: The NBDHE and the DHLOSCE was held on October 10, 2024. Dr. Waldschmidt presented information for examination users, academic programs, and faculty. A recording of this informational webinar is available below. The slide presentation (PDF) is also available for download.
View the webinar
Questions and answers about the DHLOSCE
OSCEs are widely used in the health sciences, including optometry, medicine, physical therapy, radiography, rehabilitation medicine, nursing, pharmacy, podiatry, and veterinary medicine. Since their inception in the 1970s, OSCEs are now part of the U.S. Medical Licensing Examination for all medical graduates.
THE OSCE exam format often includes stimulus materials such as radiographs, photographs, models, and prescription writing. Standardized patients (actors) have been used in medical OSCEs. The National Dental Examining Board (NDEB) of Canada uses an OSCE for dental licensure throughout the country. The exam is presented as a written, multiple-choice examination that presents stimulus materials in multiple stations. Advances in simulated patient and haptic technologies suggest that simulations may be incorporated in a dental OSCE sooner rather than later.
OSCEs were developed to help accurately assess the complex notion of clinical competence in the medical field. More specifically, Harden, Stevenson, Wilson Downie, and Wilson (1975) indicated that they introduced the OSCE format to avoid many of the weaknesses and disadvantages of traditional clinical examinations.
The JCNDE launched the Dental Licensure Objective Structured Clinical Examination (DLOSCE) in 2022 as a high-stakes clinical licensure examination for U.S. dentists. Dental boards will use examination results to help them determine whether a candidate shows the level of clinical judgment and skills needed to safely practice entry-level dentistry.
There has been tremendous interest in the creation of an OSCE exam that U.S. dental boards can use in evaluating dental hygiene candidates. Requests for an exam of this kind grew significantly in 2020, as COVID-19 shed light on the need for a valid clinical licensure exam that does not require candidates to work with live patients. The call for a dental hygiene OSCE came from many sources, including members of the academic community, state dental boards and the American Dental Hygienists’ Association, as well as test candidates themselves.
In June 2020, the JCNDE adopted a resolution directing the Department of Testing Services (DTS) to create a business plan concerning the potential development of a DHLOSCE. After DTS developed the plan, it was reviewed by several JCNDE committees, including the Committees on Administration, Dental Hygiene, Examination Development, and Research and Development. The plan was considered by the full JCNDE in June 2021, at which time development of the DHLOSCE was approved.
DHLOSCE content will be determined by subject matter experts in dentistry and dental hygiene, based on practice analysis findings and in accordance with industry best practices and professional standards such as the Standards for Educational and Psychological Testing (AERA, APA, & NCME, 2014). The JCNDE and DTS follow rigorous development procedures rooted in psychometrics, which typically require several years to execute.
DHLOSCE development is already underway, with steering and working committees established in 2021 and core content being built in 2022. Steps for 2023 include development of test items and materials such as 3D models and stimulus materials. Focused field investigations will also be conducted as needed. The examination launched in October 2025.
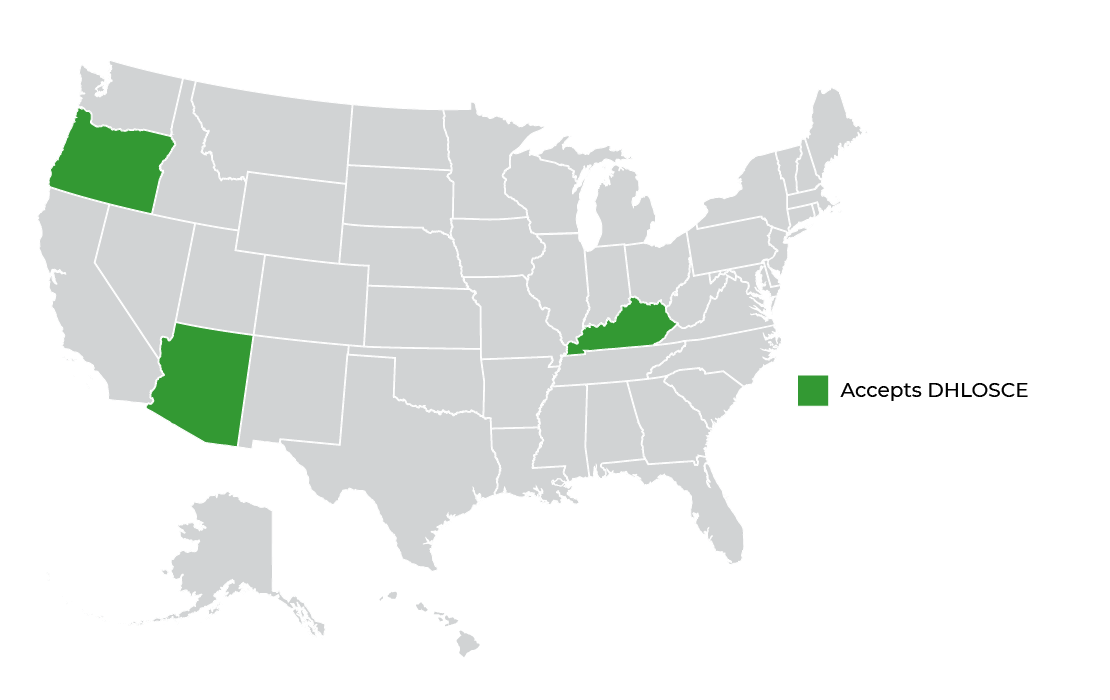
The Dental Hygiene Licensure Objective Structured Clinical Examination (DHLOSCE) is now accepted in the following states in fulfillment of board clinical licensure examination requirements. Please refer to each state board’s website for specific details, clarifications, and updated policies.
Application procedures are likely to mirror procedures currently in place for the National Board Dental Hygiene Examination (NBDHE). Candidates will register for the examination online via the JCNDE website. The examination will be offered during specific testing windows, which will be determined closer to the anticipated launch date in the 4th quarter of 2025. Please check back here for future updates.
Lend your talents to future applicants. The Department of Testing Services needs volunteer subject matter experts to assist with test construction. Volunteers may also earn CE credit.